简单介绍
G6是由蚂蚁金服体验技术部开发的图可视化引擎,提供了一系列设计优雅、便于使用的图可视化解决方案,便于开发者搭建图可视化、图分析、图编辑应用。
相关链接
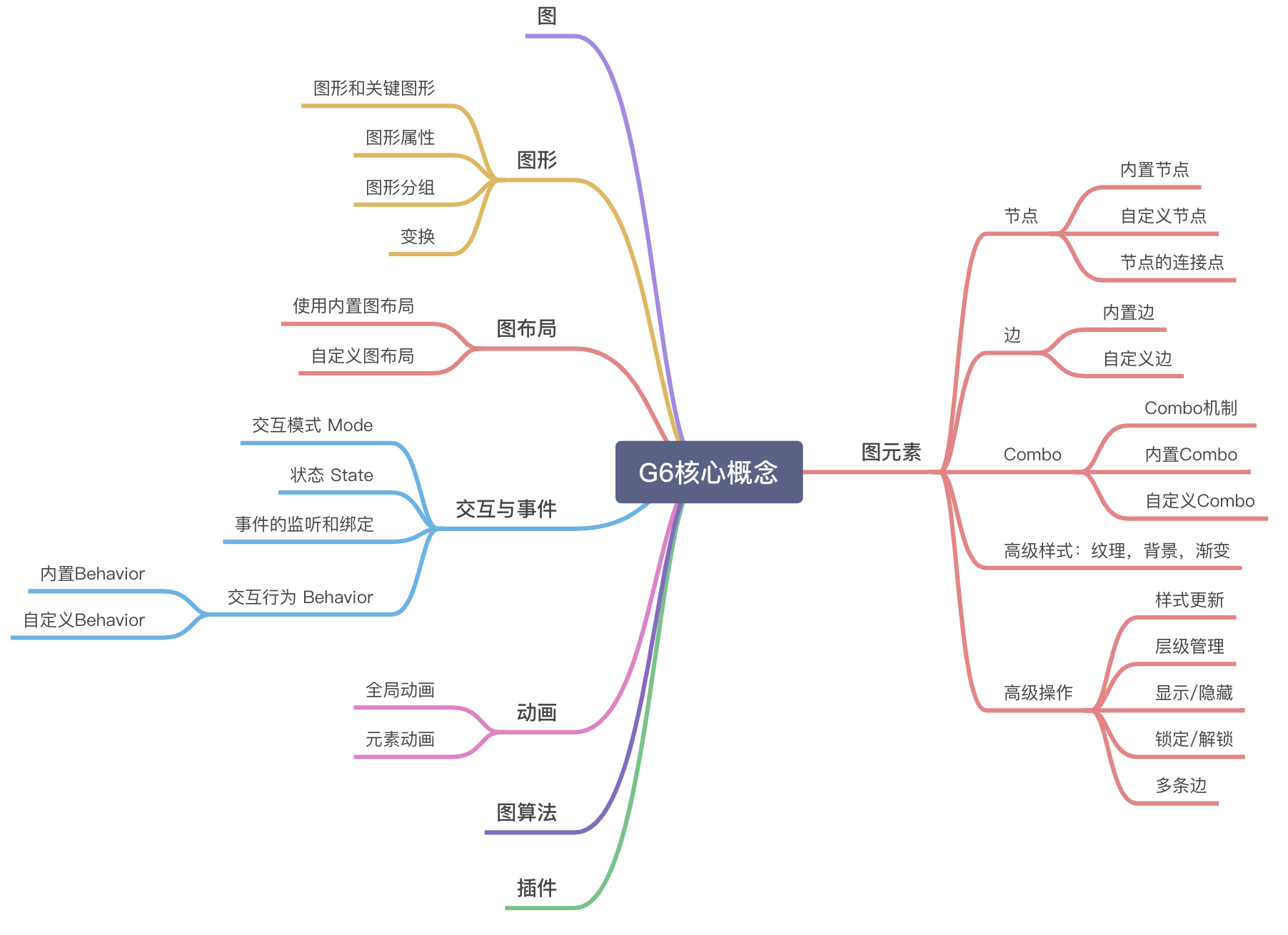
核心概念
G6中的核心概念如下方的思维导图展示:
本文作为入门教程,主要介绍一些G6中常用的概念知识:
- 图
- 图元素
- 节点
- 边
- 交互与事件
- 动画
- 插件
使用入门
第一个G6应用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Tutorial Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 图的画布容器 -->
<div id="graph"></div>
<!-- 引入 G6 -->
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/antv-g6/4.8.22/g6.min.js"></script>
<script>
// 定义数据源
const data = {
// 点集
nodes: [{
id: 'node1',
x: 100,
y: 200,
},
{
id: 'node2',
x: 300,
y: 200,
},
],
// 边集
edges: [
// 表示一条从 node1 节点连接到 node2 节点的边
{
source: 'node1',
target: 'node2',
},
],
};
// 创建 G6 图实例
const graph = new G6.Graph({
container: 'graph', // 指定图画布的容器 id,与第 11 行的容器对应
// 画布宽高
width: 800,
height: 500,
});
// 读取数据
graph.data(data);
// 渲染图
graph.render();
</script>
</body>
</html>Graph 图
主体(objects)与关系(relationships)的组成。它甚至不局限于视觉,主体与关系的数据也可以称为图。
在 G6 中,Graph 对象是图的载体,它包含了图上的所有元素(节点、边等),同时挂载了图的相关操作(如交互监听、元素操作、渲染等)。
Graph 对象的生命周期为:初始化 —> 加载数据 —> 渲染 —> 更新 —> 销毁。
<div id="graph"></div>
<script>
const graph = new G6.Graph({
container: 'graph',
width: 800,
height: 500,
});
</script>Node 节点
节点是关系图上常用的展示元素之一。
内置节点
G6 的内置节点包括 circle,rect,ellipse,diamond,triangle,star,image,modelRect,donut(v4.2.5 起支持)。
展示内置的默认节点及其样式,为每个节点设置唯一的id,并使用x,y设置节点位置,type指定节点类型,使用label展示默认的显示文本:
const data = {
nodes: [
{
id: "node_circle",
x: 100,
y: 100,
type: "circle",
label: "circle"
},
{
id: "node_rect",
x: 200,
y: 100,
type: "rect",
label: "rect"
},
{
id: "node-ellipse",
x: 330,
y: 100,
type: "ellipse",
label: "ellipse"
},
{
id: "node-diamond",
x: 460,
y: 100,
type: "diamond",
label: "diamond"
},
{
id: "node-triangle",
x: 560,
y: 100,
//size: 80,
type: "triangle",
label: "triangle"
},
{
id: "node-star",
x: 660,
y: 100,
//size: [60, 30],
type: "star",
label: "star"
},
{
id: "node-image",
x: 760,
y: 100,
size: 50,
type: "image",
img:
"https://gw.alipayobjects.com/zos/rmsportal/XuVpGqBFxXplzvLjJBZB.svg",
label: "image"
},
{
id: "node-modelRect",
x: 900,
y: 100,
type: "modelRect",
label: "modelRect"
},
{
id: "node-donut",
x: 1030,
y: 100,
type: "donut", // 节点类型
donutAttrs: {
// 甜甜圈字段,每个字段必须为 [key: string]: number
prop1: 10,
prop2: 20,
prop3: 25,
prop5: 10,
prop6: 20
},
label: 'donut'
}
]
};
const graph = new G6.Graph({
container: "graph",
width: 1500,
height: 300
});
graph.data(data);
graph.render();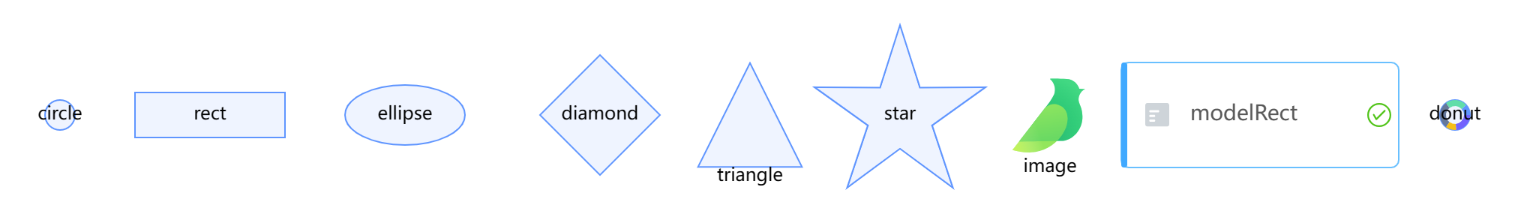
自定义节点
当内置节点无法满足实际业务需求时,可以通过G6.registerNode将自己编写的节点注册到G6中使用,registerNode总共需要三个参数:节点名称、节点配置定义、被继承节点类型。
如下是注册一个自定义的节点card-node的示例,该自定义节点继承自single-node(节点的基类),通过重写drawShape方法绘制节点。
drawShape方法共有两个参数,cfg和group,其中cfg是节点的配置对象,group是节点的图形容器。
const ICON_MAP = {
a: "https://gw.alipayobjects.com/mdn/rms_8fd2eb/afts/img/A*0HC-SawWYUoAAAAAAAAAAABkARQnAQ",
b: "https://gw.alipayobjects.com/mdn/rms_8fd2eb/afts/img/A*sxK0RJ1UhNkAAAAAAAAAAABkARQnAQ"
};
G6.registerNode(
"card-node",
{
drawShape: function drawShape(cfg, group) {
const color = cfg.error ? "#F4664A" : "#30BF78";
const shape = group.addShape("rect", {
attrs: {
x: 0,
y: 0,
width: 200,
height: 60,
stroke: color,
radius: 2
},
name: "main-box",
draggable: true
});
group.addShape("rect", {
attrs: {
x: 0,
y: 0,
width: 200,
height: 20,
fill: color,
radius: [2, 2, 0, 0]
},
name: "title-box",
draggable: true
});
// left icon
group.addShape("image", {
attrs: {
x: 4,
y: 2,
height: 16,
width: 16,
cursor: "pointer",
img: ICON_MAP[cfg.nodeType || "app"]
},
name: "node-icon"
});
// title text
group.addShape("text", {
attrs: {
textBaseline: "top",
y: 2,
x: 24,
lineHeight: 20,
text: cfg.title,
fill: "#fff"
},
name: "title"
});
if (cfg.nodeLevel > 0) {
group.addShape("marker", {
attrs: {
x: 184,
y: 30,
r: 6,
cursor: "pointer",
symbol: cfg.collapse ? G6.Marker.expand : G6.Marker.collapse,
stroke: "#666",
lineWidth: 1
},
name: "collapse-icon"
});
}
// The content list
cfg.panels.forEach((item, index) => {
// name text
group.addShape("text", {
attrs: {
textBaseline: "top",
y: 25,
x: 24 + index * 60,
lineHeight: 20,
text: item.title,
fill: "rgba(0,0,0, 0.4)"
},
name: `index-title-${index}`
});
// value text
group.addShape("text", {
attrs: {
textBaseline: "top",
y: 42,
x: 24 + index * 60,
lineHeight: 20,
text: item.value,
fill: "#595959"
},
name: `index-value-${index}`
});
});
return shape;
}
},
"single-node"
);
const graph = new G6.Graph({
container: "graph",
width: 1000,
height: 300,
defaultNode: {
type: "card-node"
}
});
const data = {
nodes: [
{
title: "node1",
error: true,
nodeType: "a",
id: "node1",
nodeLevel: 2,
panels: [
{ title: "成功率", value: "11%" },
{ title: "耗时", value: "111" },
{ title: "错误数", value: "111" }
],
x: 100,
y: 10
},
{
title: "node2",
error: false,
nodeType: "b",
id: "node2",
nodeLevel: 0,
panels: [
{ title: "成功率", value: "11%" },
{ title: "耗时", value: "111" },
{ title: "错误数", value: "111" }
],
x: 100,
y: 110
},
{
title: "node3",
error: false,
nodeType: "a",
id: "node3",
nodeLevel: 3,
panels: [
{ title: "成功率", value: "11%" },
{ title: "耗时", value: "111" },
{ title: "错误数", value: "111" }
],
collapse: true,
x: 100,
y: 210
}
]
};
graph.data(data);
graph.render();
Edge 边
内置边
G6 提供了 9 种内置边:
line:直线,不支持控制点;
polyline:折线,支持多个控制点;
arc:圆弧线;
quadratic:二阶贝塞尔曲线;
cubic:三阶贝塞尔曲线;
cubic-vertical:垂直方向的三阶贝塞尔曲线,不考虑用户从外部传入的控制点;
cubic-horizontal:水平方向的三阶贝塞尔曲线,不考虑用户从外部传入的控制点;
loop:自环。
控制点:边的拐点
下面的代码展示了如何节点之间如何利用边相连,以展示节点之间的关系:
const data = {
nodes: [
{ id: '1', x: 50, y: 50, size: 20 },
{ id: '2', x: 150, y: 50, size: 20 },
{ id: '3', x: 200, y: 50, size: 20 },
{ id: '4', x: 300, y: 130, size: 20 },
{ id: '5', x: 350, y: 50, size: 20 },
{ id: '6', x: 450, y: 50, size: 20 },
{ id: '7', x: 500, y: 50, size: 20 },
{ id: '8', x: 600, y: 50, size: 20 },
{ id: '9', x: 650, y: 50, size: 20 },
{ id: '10', x: 750, y: 50, size: 20 },
{ id: '11', x: 800, y: 50, size: 20 },
{ id: '12', x: 900, y: 150, size: 20 },
{ id: '13', x: 950, y: 50, size: 20 },
{ id: '14', x: 1050, y: 150, size: 20 },
{ id: '15', x: 1100, y: 50, size: 20 },
],
edges: [
{ source: '1', target: '2', type: 'line', label: 'line' },
{ source: '3', target: '4', type: 'polyline', label: 'polyline' },
{ source: '5', target: '6', type: 'arc', label: 'arc' },
{ source: '7', target: '8', type: 'quadratic', label: 'quadratic' },
{ source: '9', target: '10', type: 'cubic', label: 'cubic' },
{ source: '11', target: '12', type: 'cubic-vertical', label: 'cubic-vertical' },
{ source: '13', target: '14', type: 'cubic-horizontal', label: 'cubic-horizontal' },
{ source: '15', target: '15', type: 'loop', label: 'loop' },
],
};
const graph = new G6.Graph({
container: 'graph',
width: 1500,
height: 300,
linkCenter: true, // 使边连入节点的中心
});
graph.data(data);
graph.render();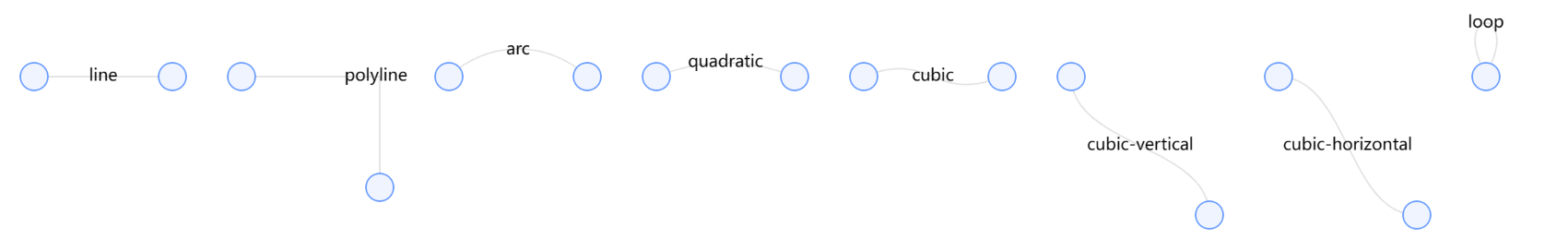
自定义边
在实际开发中,比较少需要直接开发一个新类型的边,更多的是基于现有边的扩展。
在如下的代码中,注册了一个名为circle-running的自定义边,通过重写afterDraw方法拓展了贝塞尔曲线内置边的样式,为其添加了动画,表明节点方向:
G6.registerEdge(
'circle-running',
{
afterDraw(cfg, group) {
// get the first shape in the group, it is the edge's path here=
const shape = group.get('children')[0];
// the start position of the edge's path
const startPoint = shape.getPoint(0);
// add red circle shape
const circle = group.addShape('circle', {
attrs: {
x: startPoint.x,
y: startPoint.y,
fill: '#1890ff',
r: 3,
},
// must be assigned in G6 3.3 and later versions. it can be any string you want, but should be unique in a custom item type
name: 'circle-shape',
});
// animation for the red circle
circle.animate(
(ratio) => {
// the operations in each frame. Ratio ranges from 0 to 1 indicating the prograss of the animation. Returns the modified configurations
// get the position on the edge according to the ratio
const tmpPoint = shape.getPoint(ratio);
// returns the modified configurations here, x and y here
return {
x: tmpPoint.x,
y: tmpPoint.y,
};
},
{
repeat: true, // Whether executes the animation repeatly
duration: 3000, // the duration for executing once
},
);
},
},
'cubic', // extend the built-in edge 'cubic'
);
const data = {
nodes: [
{
id: 'node1',
x: 100,
y: 100,
label: 'Node 1',
labelCfg: {
position: 'top',
},
},
{
id: 'node2',
x: 300,
y: 200,
color: '#40a9ff',
label: 'Node 2',
labelCfg: {
position: 'left',
offset: 10,
},
},
],
edges: [
{
source: 'node1',
target: 'node2',
},
],
};
const graph = new G6.Graph({
container: 'graph',
width: 1500,
height: 300,
defaultEdge: {
type: 'circle-running',
style: {
lineWidth: 2,
stroke: '#bae7ff',
},
},
});
graph.data(data);
graph.render();
交互与事件
内置交互
G6主要考虑图可视化、图编辑、图分析三个主要场景的交互行为,内置了一些通用的交互事件。
以下列举一些常用的内置交互:
- drag-canvas:拖拽画布
- zoom-canvas:缩放画布
- drag-node:拖拽节点
- click-select:单击选中/取消选中节点
- brush-select:框选节点
- create-edge:创建边
const data = {
nodes: [
{
id: "node1",
x: 100,
y: 100
},
{
id: "node2",
x: 300,
y: 100
}
],
edges: [
{
source: "node1",
target: "node2"
}
]
};
const graph = new G6.Graph({
container: "graph",
width: 800,
height: 500,
modes: {
default: [
'drag-canvas',
'zoom-canvas',
'drag-node',
'click-select',
'create-edge',
// 'brush-select'
]
},
defaultEdge: {
type: 'quadratic',
style: {
stroke: '#F6BD16',
lineWidth: 2,
},
},
linkCenter: true
});
graph.data(data);
graph.render();
// 用于处理连线重叠
graph.on('aftercreateedge', (e) => {
const edges = graph.save().edges;
G6.Util.processParallelEdges(edges);
graph.getEdges().forEach((edge, i) => {
graph.updateItem(edge, {
curveOffset: edges[i].curveOffset,
curvePosition: edges[i].curvePosition,
});
});
});自定义交互
由于场景不一样,业务不一样,同样的目的需要的交互都不一样,因此内置的交互并不能覆盖所有的需求。
以添加节点为例,自定义一个点击画布,在点击位置添加节点的交互:
G6.registerBehavior("click-add-node", {
getEvents() {
return {
"canvas:click": "onClick"
};
},
onClick(ev) {
const id = `${new Date().valueOf()}`;
this.graph.addItem("node", {
x: ev.canvasX,
y: ev.canvasY,
id: id
});
}
});监听和绑定事件
全局事件
只要在画布上范围内发生均会被触发,如 mousedown,mouseup,click,mouseenter,mouseleave 等。
获取点击对象的类型:
graph.on('click', (ev) => {
const shape = ev.target;
const item = ev.item;
if (item) {
const type = item.getType();
}
});Canvas事件
只在 canvas 空白处被触发,如 canvas:mousedown,canvas:click 等,以canvas:eventName 为事件名称。
graph.on('canvas:click', (ev) => {
const shape = ev.target;
const item = ev.item;
if (item) {
const type = item.getType();
}
});节点/边上的事件
例如 node:mousedown,edge:click, combo:click 等,以 type:eventName 为事件名称。
graph.on('node:click', (ev) => {
const node = ev.item; // 被点击的节点元素
const shape = ev.target; // 被点击的图形,可根据该信息作出不同响应,以达到局部响应效果
// ... do sth
});
graph.on('edge:click', (ev) => {
const edge = ev.item; // 被点击的边元素
const shape = ev.target; // 被点击的图形,可根据该信息作出不同响应,以达到局部响应效果
// ... do sth
});时机事件
时机事件指渲染、视口变换、元素增删改、数据变换等时机发生的事件。
例如,在图渲染完成后的处理事件:
graph.on('afterrender', (ev) => {
// ... do sth
});自定义事件
可在任意位置通过graph.emit触发自定义事件,并通过graph.on进行监听
graph.on('some-custom-event-name', (ev) => {
// ... do sth
});
graph.emit('some-custom-event-name', {
// some params
})Mode 交互模式
用户在交互一张图时,可能由于意图不同而存在不同的交互模式,例如编辑和查看模式的切换;也会因为存在冲突的交互而感到困惑,例如页面滚动和缩放画布、拖拽画布和框选、点击创建边和节点选中。
重新回顾交互式示例 – 内置交互。
为了解决上述问题,G6 提供了交互模式 Mode,它是图上交互行为的管理机制。一个图上可以有存在多种交互模式,每个交互模式包含多种交互行为。
以图编辑和查看模式的切换为例,为图设置查看和编辑两种交互模式,默认为查看交互,并可以在两种交互模式间切换:
const data = {
nodes: [
{
id: "node1",
x: 100,
y: 100
},
{
id: "node2",
x: 300,
y: 100
}
],
// 边集
edges: [
{
source: "node1",
target: "node2"
}
]
};
const graph = new G6.Graph({
container: "graph",
width: 800,
height: 500,
modes: {
default: ["drag-canvas", "zoom-canvas"],
edit: ["drag-canvas", "zoom-canvas", "drag-node", "create-edge"]
},
defaultEdge: {
type: "quadratic",
style: {
stroke: "#F6BD16",
lineWidth: 2
}
},
linkCenter: true
});
graph.data(data);
graph.render();
graph.on("aftercreateedge", (e) => {
const edges = graph.save().edges;
G6.Util.processParallelEdges(edges);
graph.getEdges().forEach((edge, i) => {
graph.updateItem(edge, {
curveOffset: edges[i].curveOffset,
curvePosition: edges[i].curvePosition
});
});
});
const selector = document.getElementById("modeSelector");
selector.addEventListener("change", (e) => {
const value = e.target.value;
if (value === "edit") {
graph.setMode("edit");
} else {
graph.setMode("default");
}
});动画
全局动画
G6 的全局动画指通过图实例进行某些全局操作时,产生的动画效果。
通过设置animate为true,并配置animateCfg动画参数实现。
例如,图居中操作:
graph.fitCenter(true, {
easing: "easeCubic",
duration: 400
});元素动画
通过注册自定义元素时,重写afterDraw方法为拓展元素样式,并为元素添加自定义动画。
插件
G6提供了一些使用的插件,在实例化插件后将其配置在plugins内即可。
以Tooltip提示框为例,便于展示节点的更多信息,同时限制了展示提示框的节点类型:
const data = {
nodes: [
{
id: "0",
label: "Has Tooltip - node0",
x: 100,
y: 50,
description: "This is node-0.",
subdescription: "This is subdescription of node-0."
},
{
id: "1",
label: "No Tooltip - node1",
x: 250,
y: 50,
description: "This is node-1.",
subdescription: "This is subdescription of node-1.",
type: "circle"
},
{
id: "2",
label: "Tooltip on Text - node2",
x: 150,
y: 210,
description: "This is node-2.",
subdescription: "This is subdescription of node-2.",
type: "circle"
},
{
id: "3",
label: "Tooltip on KeyShape - node-3",
x: 320,
y: 210,
description: "This is node-3.",
subdescription: "This is subdescription of node-3."
}
],
edges: [
{
id: "e0",
source: "0",
target: "1",
description: "This is edge from node 0 to node 1."
},
{
id: "e1",
source: "0",
target: "2",
description: "This is edge from node 0 to node 2."
},
{
id: "e2",
source: "0",
target: "3",
description: "This is edge from node 0 to node 3."
}
]
};
const tooltip = new G6.Tooltip({
offsetX: 10,
offsetY: 10,
// the types of items that allow the tooltip show up
// 允许出现 tooltip 的 item 类型
itemTypes: ["node"],
// custom the tooltip's content
// 自定义 tooltip 内容
getContent: (e) => {
const outDiv = document.createElement("div");
outDiv.style.width = "fit-content";
//outDiv.style.padding = '0px 0px 20px 0px';
outDiv.innerHTML = `
<h4>Custom Content</h4>
<ul>
<li>Type: ${e.item.getType()}</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li>Label: ${e.item.getModel().label || e.item.getModel().id}</li>
</ul>`;
return outDiv;
},
shouldBegin: (e) => {
const node = e.item
const model = node.getModel()
if (model && model.type === 'circle') {
return true
}
return false
}
});
const graph = new G6.Graph({
container: "graph",
width: 500,
height: 500,
linkCenter: true,
plugins: [tooltip],
modes: {
default: ["drag-node"]
},
defaultNode: {
size: [80, 40],
type: "rect"
}
});
graph.data(data);
graph.render();